HTTP Protocol
- was originally meant for retrieving static text based resources
- has been extended in various ways to support complex applications
- is a REQUEST-RESPONSE protocol
- is a STATELESS protocol
- uses STATEFUL TCP protocol for the transport mechanism, but HTTP itself is STATELESS
HTTP Messages (Both request & Response)
Both Requests and Responses have
- One or more headers ( each on a separate line)
- A MANDATORY blank line (CRLF)
- An OPTIONAL body.

HTTP Requests

First line of HTTP request always contains the following three items , separated by spaces
1. Method - GET - GET does not allow a message body, since it is used for requests
- POST
2. Path & query string - path is the location of the resource
- query string is to pass parameters to the resource
- query string is followed by "?"
3. Protocol - HTTP 1.0
- HTTP 1.1 - In this version the "HOST" header is mandatory
2. Path & query string - path is the location of the resource
- query string is to pass parameters to the resource
- query string is followed by "?"
3. Protocol - HTTP 1.0
- HTTP 1.1 - In this version the "HOST" header is mandatory
Other Headers in a Request
1. Referer - URL from which request originated
- the header was misspelled originally and has retained the wrong spelling
2. User-Agent -info about the software that generated the request
-MOZILLA is used as a prefix for historical reasons, to assert that the requesting browser is compatible with the "Netscape" standard.
3. HOST - specifies the hostname as the "path" in first line does not usually contain the hostname
HTTP Response

First line of HTTP response always contains the following three items, separated by spaces
1. HTTP Version - HTTP 1.0
- HTTP 1.1
2. Status code - 200 (numeric code)
3. Status Description - OK ( textual description of Status code)
Other Interesting Headers in HTTP Response
1. Server - Info about the Web Server and installed modules and OS
- Info may not be accurate
2. Set-Cookie - a further cookie , that is, a cookie to be included in future requests
3. Pragma - a response header
- directs not to store the response in cache
4. Expires - to indicates that the response content expiry date
- a date in the past means response should not be cached
What is the difference between "No-Cache" & "No-Store"
No-Cache
Response is stored in the cache, but the response should not be reused for subsequent requests without first re-validation with the server using
- if-Modified-Since,
- If-Unmodified-Since,
- If-Match,
- If-None-Match .
No-Store
- Instructs to make a best effort not to write the response to disk (i.e not to cache it).
- Provides no guarantee that it will not be written to disk.
- If sent in a request, a cache MUST NOT store any part of either this request or any response to it.
- If sent in a response, a cache MUST NOT store any part of either this response or the request that elicited it. This directive applies to both non-shared and shared caches.
Provides no guarantee that it will not be written to disk.
Reason is - the HTTP/1.1 definition makes a distinction between history stores and caches.
If the user navigates back to a previous page a browser may still show you a page that has been stored on disk in the history store
What is the difference between Pragma & Cache-Control?
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.com
Cache-Control: max-age=30
Pragma: no-cache
This will constrain HTTP/1.1 caches to serve a response no older than 30 seconds, while precluding HTTP /1.0 clients from serving a cached response.
What is the Difference between GET & POST methods?
GET Method
HEAD
CONNECTION
ORIGIN Header ( Used in Cross Origin Requests)
Referer Header
Response Headers
Access-Control-Allow-Origin
Cache Control
See above for difference between "Cache control" and "Pragma"
Etag
Expires
Location
WWW-Authenticate
- The "Pragma" header field allows backwards compatibility with HTTP/1.0 caches.
- Cache-Control was not defined until HTTP/1.1
- HTTP /1.0 clients do not understand "Cache-Control" header
- When the Cache-Control header field is also present and understood in a request, Pragma is ignored.
- Cache-Control header takes precedence in case of HTTP/1.1 ==> Pragma is ignored when both "Cache-Control" and "Pragma" are present.
- When the "Cache-Control" header field is not present in a request, caches MUST consider the "No-cache" request pragma-directive as having the same effect as if "Cache-Control: no-cache" were present.
- When sending a no-cache request, a client ought to include both the Pragma and cache-control directives in order to target both HTTP 1.0 and HTTP 1.1 caches
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.com
Cache-Control: max-age=30
Pragma: no-cache
This will constrain HTTP/1.1 caches to serve a response no older than 30 seconds, while precluding HTTP /1.0 clients from serving a cached response.
What is the Difference between GET & POST methods?
GET Method
- Designed to retrieve resources
- Can be used to send parameters in the query string of the URL
- GET requests can be bookmarked and reused later.
- "GET-Request-URL" is displayed on screen
- GET requests get logged in browser history & Web Server's access log
- GET requests can be cached, if "no-store" directive is not present.
- "GET-Request-URL" is also sent to other sites in "Referer" header.
- GET Requests should NOT BE USED to transmit sensitive information.
- The semantics of the GET method change to a "conditional GET" if the request message includes an If-Modified-Since, If-Unmodified-Since, If-Match, If-None-Match
- GET Request has Length Restrictions ( 2048 characters)
- GET Request does not have a BODY
- Only ASCII encoding is allowed ( Encoding type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded)
- Hitting "Back Button" will simply resubmit the GET Request
- Designed to perform "Actions".
- Parameters can be submitted using both the URL Query String as well as using Message Body Parameters submitted using the Message Body ( not the Query String) will not be logged on Server or in Browser History.
- Hitting Back button will alert the user that the Data will be resubmitted and ask for confirmation.
- POST Request cannot be bookmarked (POST request URL can still be Bookmarked)
- No restrictions on type of data, even Binary is allowed (multipart/form-data)
- No length restrictions
HEAD
- Returns the HEAD of the Response to corresponding GET Request
- Aim is to check if the resource exists on the server
- Server's response = (Response to a GET request) MINUS (The body)
- Server returns the same headers as it would for a GET Request
- Used for diagnostics
- Server returns the exact "REQUEST" message it received.
- Used to detect the effect of Proxy servers that manipulate the request
- Returns the list of Methods supported for a particular Resource
- Response contains "Allow" Header
- Eg. Allow : GET, POST , PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS
- Attempts to upload the specified resource to the server
- Content to be uploaded is in the Request Body
- Can be used to attack the Application.
- scheme://domain:port/path?query_string#fragment_id
- SCHEME is mostly the protocol ( but not always)
- PORT is OPTIONAL
- PORT is used when it differs from the Default Port used by the Protocol
- PATH is specified using /a/b/c/ and is OPTIONAL
- QUERY STRING starts with "?"
- QUERY STRING contains "name=value" pairs separated by Ampersand (&)
- FRAGMENT ID starts with "#", but "#" is not a part of the Fragment ID
- FRAGMENT ID identifies a portion of the document
- FRAGMENT ID is not sent to the server along with the GET Request
- FRAGMENT ID is processed fully on the client side
- A style of Architecture meant for distributed systems
- In REST "Requests & Responses" both contain "Representation of the State" of the system (Example: HTTP)
- World wide web (HTTP Protocol, URL format) conforms to REST Architecture
- REST- URL is a UNIQUE identifier for the resource being accessed.
- The HTTP Methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) describe the operations to be performed on the resource addressed by the Unique URL.
- URL containing its parameters within the URL file path rather than the Query String
- http://example.com/search?os=android&model=nexus4
- [Above is a Normal URL, though it is still conforms to REST]
- http://example.com/search/android/nexus4
- [REST style URL]
CONNECTION
- Whether to keep the TCP connection open or close it
- Type of encoding (Gzip) used in to compress the Response Body
- Length of Message Body.
- In case of "HEAD" Method, Content Length tells the length of corresponding GET Method
- Type of content contained in message body (text/html)
- Chunked
- Transfer-Encoding HTTP header in used in place of the Content-Length header
- Senders can begin transmitting dynamically-generated content before knowing the total size of that content.
- Types of CONTENT (image, docs) the client is willing to accept
- Types of content encoding the client is willing to accept.
- Used to submit the credentials for one of the HTTP Authentication types
- Specifies the name of the host that appears in URL being requested
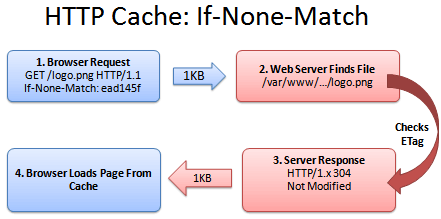
- To check if the resource has changed since the last request, if not, then server may allow use of Cached copy.
- Response code 304 will mean => Use the cached copy
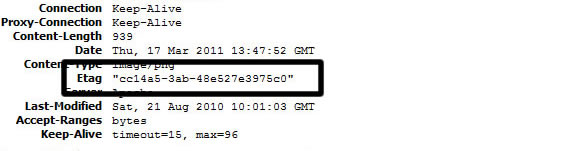
- Specifies an Entity tag ( a string identifier)
- Client submits the Etag along with request
- Etag is used to identify the version of resource.
- If client "Etag" from client matches current version => Response code 304
- Response code 304 will mean => Use the cached copy
ORIGIN Header ( Used in Cross Origin Requests)
- Used in cross domain requests to indicate the domain (only the domain name) from which request originated
Referer Header
- Gives the complete URL from which request originated
Response Headers
Access-Control-Allow-Origin
- Part of HTTP CORS (Cross site request Standard)
- Indicates the sites from which a resource can be accessed via XMLHTTPRequest (AJAX)
- Earlier, HTTP Requests generated by Scripts could only be sent to the origin domain.
Cache Control
- Passes caching directives
See above for difference between "Cache control" and "Pragma"
Etag
- Specifies an entity Tag (is received in a Response)
- Is used to track the version of the resource
- Is sent back to server using "If-None-Match" header
- If Etag of a resource is the same, then a cached copy can be used
Expires
- Server the duration for which the resource can be cached, using this header.
Location
- Used in Redirection Responses (Responses with 3xx Status code)
- Identifies the location of the Redirect

WWW-Authenticate
- Sent along with a 401 (Not authorized) response
- Provides the details of types of authentication the server supports
- Client sends the authorization values using "Authentication" Header
X-Frame-Options
- Used to protect against ClickJacking
- Declares a policy (communicated from server to client browser)
- Declares whether the client browser may display that response in an <IFRAME> which is part of other web-pages
- Values: DENY, SAMEORIGIN, ALLOW-FROM
Cookies
- Are Data Values stored on client, by the server
- Are sent to server along with every request
- Can be used to exploit vulnerabilities
- Are name-value pairs, the value of cookie, does not contain "spaces"
- Cookie is set using "Set-Cookie" Header
- Multiple cookies require multiple "Set-Cookie" Headers
"Set Cookie Header" can have following OPTIONAL ATTRIBUTES
- Expires: The date until which cookie is valid.
- Expires: Future Expiry => cookie is stored in persistent storage, and is reused later browser sessions,
- Expires: If not set => the cookie is only valid for current browser session.
- Domain: The domain for which cookie is valid
- Domain: Must be same as or subdomain of parent domain
- Path: URL Path for which cookie is valid
- Secure: Cookie is transmitted over HTTPS Only
- HTTPONLY: Cookie cannot be accessed by Client Side Javascript (For XSS Prevention)
HSTS : HTTP STRICT TRANSPORT SECURITY
- An opt-in Security Enhancement
- Specified by a web application using "Strict-Transport-Security" Response Header
- Once this Header is received, then all future communication is sent on HTTPS
- Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains
- Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload
- Max-Age: applicable for duration
- includeSubDomains: all subdomains should be served on HTTPS
- preload: Site owners can sign-up to get their domain on HSTS Preload list maintained by Major browsers
Status Codes
1xx : Informational
2xx: Successful ( 200 OK)
3xx: Redirection related
4xx: Error of some Kind
5xx: Server Error of some kind
100 CONTINUE
- Initial Request: Client sends Header - "Expect: 100-continue" , To determine if server is willing to accept a request (based on the request headers) before the client sends the body, to check the legitimacy of the Request (Example : POST)
- Server Responds with 100 CONTINUE or else 417 EXPECTATION FAILED
200 OK
- Request is Successful
301 Moved Permanently ( Redirect Related)
- Redirect THIS and ALL FUTURE requests to a URL specified by the "Location Header" in Response
302 Found (Redirect Related)
- Temporary Redirect to a URL Specified in "Location Header"
304 Not Modified ( Redirect Related)
- Instructs to use the cached copy stored on client
400 Bad Request
- Invalid Request (Probably malformed)
401 Unauthorized
- Server requires HTTP Authentication
- Server response will contain - "WWW-Authenticate header"
- "WWW-Authenticate" Header will give details of supported authentication types
403 Forbidden
- No one is allowed to access this resource, regardless of authentication
404 Not Found
- Resource does not exist
405 Method Not Allowed
- Method Used (Eg. PUT, DELETE) is not supported by specified URL
413 Request Entity is Too Large
- The "Request" sent is too large to Handle
414 Request URI Too Long
- Request URL is too long
500 Internal Server Error
- Server Encountered an error
- May be because of an unexpected Input caused unhandled error
- See server's full response for details
503 Service Unavailable
- Server is working, but the backend application is not working
- Try to identify if one of your actions caused this.
What is HTTPS? - HTTP Secure
- HTTP uses TCP as its transport mechanism
- HTTP is unencrypted and can be intercepted
- HTTPS is essentially HTTP tunneled over SSL.
- SSL protects Confidentiality & Integrity of underlying HTTP Traffic
- HTTPS Prevents eavesdropping & MITM Attacks
- HTTPS also provides Authentication of the Website & WebServer
- A site must be Entirely hosted over HTTPS
- Partially loading some of the content (Scripts & CSS) on HTTP, makes the user vulnerable to attacks.
- Cookies on an HTTPS site should have "Secure" Flag Set
- SSL uses long-term public and secret keys to generate a short term session key to encrypt the data flow between client and server
A in CIA = Availability ( not Authentication)
HTTP Authentication
HTTP Protocol has its own mechanism to authenticate users. This is mostly used over Intranet only
Basic
- credentials are sent in base64 encoded string
- credentials are sent with each request
- Should only be used over HTTPS
NTLM
- Uses a challenge/response mechanism to avoid password capture or replay attacks
Digest
- credentials are sent as MD5 hash
- HASH is calculated using a NONCE & Password
- NONCE is used to avoid replay attacks
Web Application Technologies
- Web Applications use multiple technologies to delivery their functionality.
- To be able to attack a Web application, understand how various components work together.
- Understand the weakness of each component
Server Side Functionality
- Server serves both static & dynamic resources.
- Dynamic resources - Generated by scripts,
- Scripts - take input and give an output
- Input is in the form of parameters
- Parameters allows the scripts to tailor the output to the individual user.
Parameters are sent to the application in following ways
- URL Query String
- REST-Style URL's file path
- HTTP Cookies
- Request Body (POST method)
Additionally
- Any part of HTTP Request can be used as an Input for processing Eg - User-Agent
Technologies Used on Server Side
- Scripting Languages ( PHP, Perl )
- Application Platform (Java, ASP.NET)
- Web Server - IIS, Apache
- Database - MYSQL, MS-SQL, Oracle
- Other Backend Components - SOAP-based Web Service, Directory Service
Source of many web vulnerabilities
- Application Design
- Third party packages
Some commonly Used Technologies
1. Java Platform ( Application Platform)
WAS de-facto for large scale enterprise applications
Long history & widely adopted = > Many high quality dev tools, app servers & frameworks available
Can be run on several OSes
Important Terms
Enterprise Java Bean ( EJB )
- A heavyweight software component
- Encapsulates a business function or logic
- Intended to handle concerns like - persistence, transactional Integrity & Security
Plain Old Java Object (POJO)
- An ordinary Java Object
- POJO refers to User defined Objects
- Much simpler than EJB
- Lightweight compared to EJB
Java Servlet
- An Object that resides on an application Server
- Processes HTTP Requests & HTTP Responses
WEB Container
- An engine which provides run-time environment for Java-based web applications
- Example : Apache Tomcat, WebLogic, JBoss
Java is well suited for modular approach. Many open source, third party components exist to help reduce development time
Examples
- Authentication Module - JAAS, ACEGI
- Presentation Layer - SiteMesh, Tapestry
- Database Object Relational Mapping - Hibernate
- Logging - Log4J
To attack: Identify the component being used, download it and try to find a vulnerability in the component and use it to attack the application.
2. PHP
- Personal Home Page
- Highly powerful and rich framework for web applications
- Used in conjugation with other technologies
- Ex: LAMP ( Linux, Apache, My SQL, PHP)
Many Open Source components exist for
- Bulletin Boards: PHPBB, PHP-Nuke
- Admin Front Ends: PHPMyAdmin
- Webmail: SquirrelMail, IlohaMail
- Photo galleries: Gallery
- Shopping Carts: osCommerce, ECW-Shop
- Wikis- MediaWiki, WakkaWikki
Design & default config of PHP framework makes it easy to unintentionally introduce security bugs
PHP Platform itself have several bugs
These bugs can be used to attack PHP Application
3. XML (Extensible Markup Language)
- Specification to encode "DATA" in both human & Machine readable form.
- XML document contains - DATA & MARKUP
- Extensible means - XML allows arbitrary tags & attribute names
- Data Type Definition (DTD) - Information contained in XML Document, which describes the Tags and attributes used in the XML Document.
- XML is used extensively in web applications
Web Services
- Web application Vulnerabilities are equally applicable to Web Services
- A web service is a "method of communication" which allows two software systems to exchange DATA over Internet
- Service Requester - requests the data
- Service Provider - processes request & provides the data
- Service provider & Requester often use different programming language
- Web Service is thus a "Method to exchange Data".
- Web Service uses two methods to exchange data
1. SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol)
2. REST (Representational State Transfer)
- SOAP uses HTTP protocol to transmit messages
- SOAP uses XML to represent the data (Content-Type: application / soap+xml)
- Using user-supplied-data in SOAP messages can lead to vulnerabilities.
- Directly exposed web-services are worthy of vulnerability examination
- WSDL (Web Services Description Language) file describes the following
-How to call the web service
-What parameters it expects
-What data structure it returns
- Tools for testing WEB Service Testing - SoapUI
Web Service ( on the Left )
SOAP Request (on the Right)


What is the difference between SOAP Web Service & REST Web Service ? ( Interview Question)
RESTful Web Services
- is faster compared to SOAP Web Services
- using REST for a Web Service is a recent trend
- does NOT NECESSARILY have to use XML
- Easy & Lightweight to use RESTful Web Service
- RESTful Web Service is STATELESS
- provides CACHING over HTTP GET method ( improves efficiency)
- has no standard set of Rules to describe the Web Service Interface.
- Client should already know what to expect from the web-service
- Resource is accessed using a UNIQUE URL
- Easy to Integrate with Existing websites
- has a small learning curve compared to REST
SOAP based Web Services
- uses XML to fetch the DATA.
- provides WSDL to specify the interface of the web-service
- allows a mechanism to describe the web-service and advertise its existence.
- useful for complex operations and those which require maintenance of STATE.
- SOAP supports multiple protocols ( REST mostly uses HTTP)
- SOAP has a bigger learning curve
Client Side Functionality ( Small Notes )
Document Object Model (DOM)
- A programming interface for HTML documents.
- Can be used to QUERY the HTML document & MODIFY it through API.
- can access HTML elements by ID.
- can traverse the HTML document.
- can be used to Read & Update Cookies.
- is Manipulated by AJAX to dynamically updated the page.
AJAX ( Asynchronous Javascript and XML)
- used to avoid full page reload
- performs an "in the background" HTTP Request & updates the page
- "XMLHttpRequest" object is used to make AJAX requests
- Allows arbitrary content to be sent ( not only XML)
- uses Synchronous method when it makes sense to make the user wait for the response
- increases the attack surface & has historically introduced some vulnerabilities.
What is Same Origin Policy ?
- Security policy implemented by browsers
- DISALLOWS content coming from one origin from accessing content coming from another origin.
- defines ORIGIN as = Protocol + host + port ( all three should match)
- -- A subdomain is considered a different host
Subtle Points of Same origin policy
- A page on domain A can send a request to domain B, but cannot process the response within the context of domain A.
- page from domain A can load a script from domain B and execute it within the context of domain B
- page on domain A cannot modify the cookies or other DOM data of domain B
Encoding Schemes
URL Encoding
- To safely transport characters over HTTP
- URLs can have only printable ASCII characters
- Prefix % followed by "ASCII code expressed in Hexadecimal"
- %25 = %
- %0D = Carriage Return
- %0A = New Line
- = Null Byte
- + = Space
- %20 = Space
To attack: URL encode "space" ? % & ; + # if you submit them as data
Unicode Encoding
- Supports all the world's writing systems
- it is a 16 bit encoding scheme
- Prefix is "%u" Suffix is hexadecimal of the character "Unicode"
UTF-8
- Variable length encoding
- uses one or more bytes to represent each character
- each byte of the UTF-8 is encoded and Prefixed with %
- Eg: %e2%89%a0 is a single character
HTML Encoding
- to represent "metacharacters" as "content" within HTML document
- < <
- > >
- Any character can be HTML encoded as follows
- A (Notice, the additional #)

Such a useful information. I'd definitely share it with my folks.Thank you!!
ReplyDeleteRemove Ripoff Report from Google:
Remove Ripoff Report
Delete Ripoff Report
Cheaterland Removal Google
How to remove Ripoff Report from Google
Ripoff Report Removal Services
I think there is a need to look for some more information about useful aspects of Power BI and Soap.
ReplyDeletePowerbi Read Soap
ACTIVE & FRESH CC FULLZ WITH BALANCE
ReplyDeletePrice $5 per each CC
US FRESH, TESTED & VERIFIED SSN LEADS
$1 PER EACH
$5 FOR PREMIUM
*Time wasters or cheap questioners please stay away
*You can buy for your specific states too
*Payment in advance
CC DETAILS
=>CARD TYPE
=>FIRST NAME & LAST NAME
=>CC NUMBER
=>EXPIRY DATE
=>CVV
=>FULL ADDRESS (ZIP CODE, CITY/TOWN, STATE)
=>PHONE NUMBER,DOB,SSN
=>MOTHER'S MAIDEN NAME
=>VERIFIED BY VISA
=>CVV2
SSN LEADS INFO
First Name | Last Name | SSN | Dob | Address | State | City | Zip | Phone Number | Account Number | Bank NAME | DL Number | Home Owner | IP Address |MMN | Income
Contact Us
-->Whatsapp > +923172721122
-->Email > leads.sellers1212@gmail.com
-->Telegram > @leadsupplier
-->ICQ > 752822040
*Hope for the long term deal
*If you buy leads in bulk, I'll definitely negotiate
*You can ask me for sample of Lead for demo
US DUMP TRACK 1 & 2 WITH PIN CODES ALSO AVAILABLE